
Tourism maps: difference between artistic, 3D satellite and 2D maps for trekking and biking
Table of Contents
Choosing the right type of map is essential in tourism, especially when it comes to outdoor activities like trekking and biking. From hand-drawn artistic maps to simple digital versions, from realistic 3D satellite views to traditional 2D maps, each option has its strengths and limitations. While some maps are visually striking and ideal for promotion, others are designed to be reliable navigation tools. In this article, we’ll explore the main differences between artistic, 3D satellite and 2D tourist maps to understand which ones are truly useful for travelers and outdoor enthusiasts.
Artistic maps for tourism: beauty and limits
Hand-painted maps are real works of art: they convey emotions, enhance a territory and can be used as exclusive promotional material. However, they have two major drawbacks:
- Very high costs, often out of budget for large-scale tourism projects.
- Limited practical use, as they are beautiful to look at but not suitable for orientation on trails, routes or complex areas.
These maps work well as gadgets, posters or decorative elements, but not as a real navigation tool.
Simple digital maps: when they are useful

Basic computer-generated maps are suitable for representing simple situations, such as:
- the plan of a small town,
- small urban areas,
- schematic maps for events or fairs.
They are inexpensive and quick solutions, but not suitable for detailed representation of large territories such as mountains, rivers, valleys and natural trails.
3D satellite maps: visual appeal but little usability

Maps with realistic satellite textures offer a spectacular overview: they show mountains, lakes and valleys in a three-dimensional and realistic way. They can be useful to provide a panoramic vision of the territory, but they present some problems:
- Limited quality: when zoomed in, they often pixelate and lose sharpness.
- Low practicality: they don’t allow following trails or planning routes for trekking or biking.
- Lack of useful details: they miss clear indications of elevation changes, points of interest, shelters and marked paths.
2D tourist maps: the ideal tool for trekking and biking
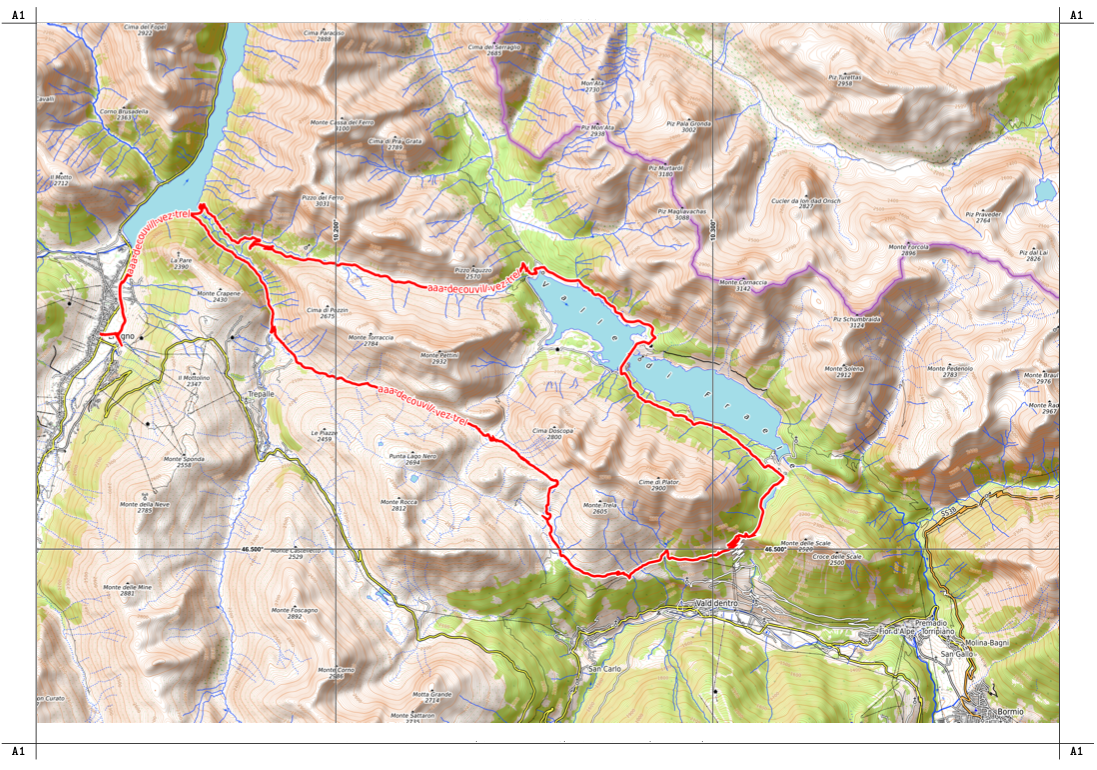
For those who practice trekking, mountain biking or hiking, classic 2D maps remain the most useful tool. Compared to other types they offer:
- Clarity and readability: trails, rivers, elevation lines and points of interest clearly highlighted.
- Reliability: based on official cartography or accurate surveys.
- Versatility: they can be printed, used digitally or integrated into apps.
In short, 2D maps may not have the scenic impact of 3D satellite maps, but they guarantee real usefulness in the field.
Conclusion: how to choose the right map for tourism
The choice of map depends on the goal:
- Artistic maps → excellent for promotion and cultural enhancement.
- Simple digital maps → useful to outline small areas.
- 3D satellite maps → fascinating but not practical for hiking.
- 2D tourist maps → the most effective for trekking, biking and outdoor activities.
A complete tourism project may also combine multiple types: 3D for visual promotion and 2D as a real support for users.
FAQ about tourism maps
Which maps are best for trekking?
Classic 2D maps, because they show trails, elevation changes and points of interest.
Are 3D satellite maps useful for orientation?
No, they are nice to look at but impractical for following routes on the ground.
Is it worth investing in an artistic map?
Yes, if the goal is promotional or cultural, but not for hiking.
Are simple digital maps suitable for tourism?
Only for very limited areas or schematic representations.
What is the most complete solution for a tourist area?
A mix: 3D satellite maps for promotion and detailed 2D maps for hikers.